Optimizing Learning Through Intelligent Feedback Mechanisms
Understanding the Need for Intelligent Feedback in Medical Education
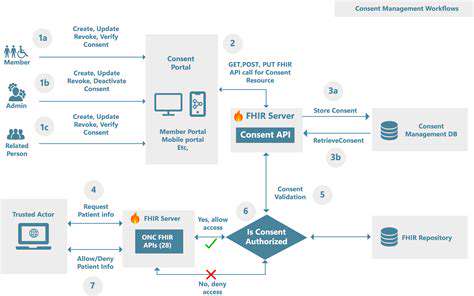
Continuing medical education (CME) is crucial for maintaining and enhancing the skills and knowledge of healthcare professionals. However, traditional CME methods often lack the personalized and adaptive feedback necessary for optimal learning. This deficiency can lead to inconsistent knowledge retention and application, potentially impacting patient care. Intelligent feedback mechanisms address this gap by providing tailored responses, identifying knowledge gaps, and offering targeted learning resources, ultimately improving the effectiveness of CME programs.
The complexity of modern medicine demands continuous learning and adaptation. Healthcare professionals need to stay abreast of advancements in diagnostic techniques, treatment protocols, and evolving patient needs. Intelligent feedback systems can play a pivotal role in facilitating this learning process by providing real-time assessment and actionable insights.
Personalized Learning Paths through Adaptive Algorithms
Intelligent feedback systems leverage sophisticated algorithms to analyze learner responses and tailor the learning path accordingly. This personalized approach ensures that individuals receive the most relevant and effective content based on their specific needs and learning style. By identifying knowledge gaps and strengths, the system can dynamically adjust the difficulty and focus of subsequent learning modules, leading to a more efficient and engaging learning experience.
Real-Time Assessment and Immediate Feedback
Traditional CME methods often rely on delayed feedback, which can hinder the learning process. Intelligent feedback mechanisms, however, provide real-time assessment and immediate feedback on learner responses. This immediate reinforcement allows for quicker identification of misconceptions and facilitates the immediate application of corrective measures. This rapid feedback loop accelerates the learning process and promotes a more active and engaged learning environment.
Targeted Remediation and Knowledge Reinforcement
When learners demonstrate a weakness in a particular area, intelligent feedback systems can pinpoint the exact knowledge gap and offer targeted remediation resources. These resources can include interactive simulations, targeted learning modules, or access to relevant research articles. This targeted approach ensures that learners gain a thorough understanding of the subject matter, strengthening their knowledge base and improving their application of learned concepts.
Enhancing Engagement and Motivation through Gamification
Integrating gamification elements into intelligent feedback systems can significantly enhance learner engagement and motivation. Features like points, badges, leaderboards, and interactive challenges can create a more dynamic and stimulating learning environment. This approach fosters a sense of accomplishment and encourages active participation, further promoting knowledge retention and skill development.
Integrating AI into Existing CME Platforms
Implementing intelligent feedback mechanisms into existing CME platforms can be a relatively smooth transition. Integrating these features into current workflows and educational resources can ensure a seamless learning experience for healthcare professionals. This integration can also leverage existing infrastructure and data to improve the accuracy and effectiveness of the feedback systems, leading to a more comprehensive and efficient CME program.

Future Trends and Challenges in AI-Powered CME

Ethical Considerations in AI Development
As AI systems become more sophisticated and integrated into various aspects of our lives, ethical considerations are paramount. Ensuring fairness, transparency, and accountability in AI algorithms is crucial to prevent unintended biases and discriminatory outcomes. Developers and policymakers must actively address potential harms and strive to create AI systems that benefit all members of society, not just a select few.
Furthermore, the potential for misuse of AI technology, such as in autonomous weapons systems or deepfakes, requires careful consideration and robust regulations. Establishing clear ethical guidelines and frameworks for AI development and deployment is essential to mitigate these risks and ensure responsible innovation.
The Impact of AI on the Workforce
AI-driven automation has the potential to significantly alter the job market. While some jobs may be displaced by automation, new roles and opportunities may emerge in areas such as AI development, maintenance, and ethical oversight. Adapting education and training programs to equip individuals with the skills needed for the future job market is essential to ensure a smooth transition.
It's crucial to recognize that the impact of AI on the workforce will not be uniform across all sectors and demographics. Careful consideration must be given to the potential for job displacement and the need for reskilling and upskilling initiatives to support affected workers.
Advancements in AI Hardware and Software
Continuous advancements in AI hardware, such as specialized processors and increased computing power, are driving progress in various fields. These advancements are enabling more complex AI models and algorithms to be developed and deployed, leading to improved performance and accuracy in tasks such as image recognition, natural language processing, and machine learning.
Concurrent improvements in AI software, including sophisticated algorithms and open-source frameworks, are making AI more accessible and user-friendly. This accessibility empowers researchers, developers, and businesses to leverage AI technologies to solve problems and create innovative solutions across a wide range of applications.
The Role of Data in AI Success
The success of AI systems heavily relies on the quality and quantity of data used for training and development. Gathering, cleaning, and labeling large datasets is a significant challenge, requiring substantial resources and expertise. Ensuring data privacy and security is paramount, especially with the increasing volume and sensitivity of data being collected and utilized.
Furthermore, biases present within data can be inadvertently perpetuated in AI systems, leading to unfair or discriminatory outcomes. Strategies for identifying and mitigating these biases in data are crucial for developing responsible and equitable AI applications.