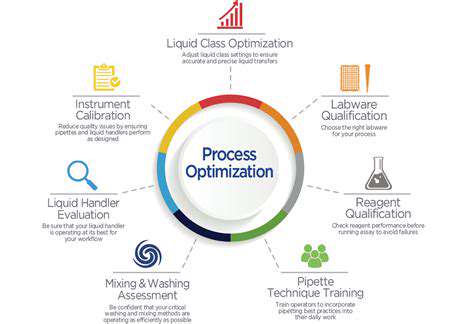
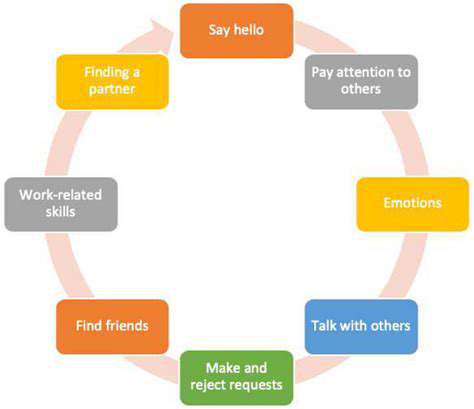
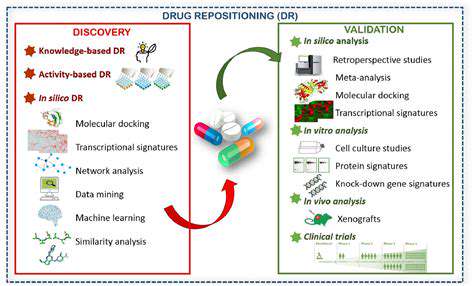
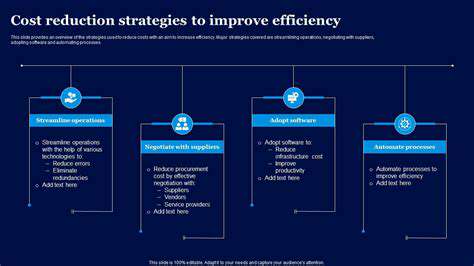
Introduction to Edge Computing in Manufacturing
Understanding the Fundamentals of Edge Computing
Edge computing represents a transformative approach to processing data, positioning computational resources near the point of data creation rather than relying solely on distant cloud servers. In the manufacturing sector, this innovation enables data from sensors, machinery, and other devices to be processed directly at their source. This eliminates the delays and bandwidth limitations associated with transmitting data to centralized data centers, offering real-time insights and faster response mechanisms crucial for enhancing production efficiency in modern manufacturing environments. This localized processing is indispensable for optimizing operations and maintaining competitiveness.
Real-Time Data Processing and Analysis
A key benefit of edge computing in manufacturing lies in its capacity for real-time data analysis. This capability empowers manufacturers to promptly detect and resolve issues, minimizing downtime and boosting operational efficiency. By analyzing data at the edge, manufacturers gain deeper insights into equipment performance, predict potential failures, and optimize production schedules dynamically. The speed and flexibility of this real-time analysis are vital for staying ahead in today's fast-paced industrial landscape.
Improved Operational Efficiency and Productivity
Edge computing significantly enhances operational efficiency by reducing latency and accelerating data processing. This enables manufacturers to streamline production lines, enhance quality control, and reduce waste. The ability to make data-driven decisions swiftly leads to increased productivity and lower operational costs. The enhanced visibility and control provided by edge computing are essential for driving continuous improvement and maintaining a competitive edge.
Enhanced Safety and Security in Manufacturing Environments
Edge computing improves safety in manufacturing by enabling real-time monitoring of critical machinery and processes. This constant vigilance allows for rapid anomaly detection and proactive hazard prevention, ensuring a safer work environment. Additionally, edge computing bolsters security by minimizing the need to transmit sensitive data over potentially insecure networks. Securing data at the edge reduces the risk of breaches and strengthens overall system resilience.
Future Trends and Applications in Smart Manufacturing
The future of edge computing in manufacturing is bright, with ongoing advancements expanding its applications. Future trends include predictive maintenance, automated quality control, and enhanced supply chain management. Integration with technologies like artificial intelligence and machine learning will unlock further optimization and innovation, driving the evolution of smart manufacturing. This synergy will create more efficient and resilient industrial ecosystems.
Enhanced Data Security and Privacy with Edge Computing
Improving Data Integrity at the Source
Edge computing significantly enhances data integrity by processing information closer to its origin. This reduces the risk of data corruption or loss during transmission. Localized validation ensures that only reliable data reaches central systems, bolstering accuracy and trustworthiness. Edge devices also implement robust encryption and access controls, strengthening overall data security.
Strengthening Privacy through Decentralized Processing
Edge computing promotes decentralized data processing, safeguarding user privacy by minimizing the transfer of sensitive data across networks. Localized computations give users greater control over their data, aligning with modern privacy regulations. Strict access controls at the edge further reduce the risk of privacy violations.
Real-time Threat Detection and Response
Edge computing enables real-time threat detection by analyzing data locally, allowing for immediate responses to potential security breaches. This rapid mitigation minimizes the impact of malicious activities, ensuring system integrity. Built-in anomaly detection algorithms adapt to evolving threats, maintaining robust security.
Reduced Reliance on Centralized Infrastructure
Edge computing offloads processing tasks to distributed edge devices, reducing dependency on centralized servers. This distributed architecture enhances system resilience, ensuring critical applications remain operational even during central infrastructure failures. This approach improves system availability and responsiveness.
Scalability and Adaptability of Security Measures
Edge computing architectures are scalable, allowing for the deployment of additional devices as needed. This flexibility enables organizations to adapt security measures to evolving threats and business requirements. The modular design facilitates the integration of advanced security technologies without disrupting operations.
Improved Data Security in IoT Environments
In IoT environments, edge computing enhances security by processing data closer to its source, reducing the exposure of sensitive information to cyber threats. Specialized security measures tailored to IoT devices address unique vulnerabilities, strengthening the IoT ecosystem.