The Expanding Landscape of IoT Connectivity
Urban centers worldwide are witnessing a quiet revolution as the Internet of Things (IoT) weaves itself into the fabric of city infrastructure. This network of interconnected devices isn't just changing how we live—it's fundamentally altering how cities breathe, function, and evolve. From traffic lights that communicate with emergency vehicles to garbage bins that signal when they need emptying, IoT is creating cities that think and respond in real-time.
Consider how water management systems now use sensors to detect leaks before they become floods, or how streetlights adjust brightness based on pedestrian activity. These aren't futuristic concepts—they're happening now in cities from Singapore to Barcelona. The true power lies not in individual devices, but in how they work together to create intelligent urban ecosystems.
Data: The Lifeblood of Smart Cities
At the heart of every smart city initiative lies data—vast quantities of it. Sensors embedded in pavement measure foot traffic, while air quality monitors track pollution levels block by block. This constant stream of information allows city planners to make decisions based on evidence rather than estimates.
Take parking management as an example. Sensors in parking spots relay availability to drivers' phones, reducing congestion caused by circling vehicles. The same data helps cities understand parking patterns, informing decisions about future garage construction or public transit expansion. It's this marriage of immediate utility and long-term planning that makes IoT data so valuable for urban management.
Security in an Interconnected Urban Landscape
With great connectivity comes great responsibility. A city's IoT network is only as strong as its most vulnerable device. Recent incidents have shown how hacked traffic systems or compromised surveillance cameras can create chaos. Municipalities must implement defense-in-depth security strategies that protect both data and physical infrastructure.
Singapore's approach offers a model—deploying quantum-resistant encryption for critical infrastructure while maintaining air-gapped backup systems. Regular penetration testing and firmware updates create multiple layers of protection. Perhaps most importantly, cities must balance security with accessibility, ensuring emergency services can override systems when lives are at stake.
From Theory to Pavement: IoT in Action
Barcelona's smart irrigation system demonstrates IoT's practical benefits. Soil moisture sensors communicate with weather forecasts to water parks only when needed, saving 25% of the city's water budget. Meanwhile, Copenhagen's intelligent street lighting has reduced energy consumption by 57% while improving public safety.
These examples reveal a crucial truth: successful IoT implementation requires aligning technology with specific urban challenges. A solution that works for Tokyo's dense population might not suit Houston's sprawl. The key lies in customizing applications to local needs while maintaining interoperability standards.
The Next Urban Frontier
As 5G networks roll out globally, IoT capabilities will expand exponentially. Imagine waste trucks that reroute in real-time based on sensor data, or bridges that warn engineers about structural fatigue before visible cracks appear. We're entering an era where city infrastructure becomes predictive rather than reactive.
The coming decade will see AI and IoT merge more completely, creating systems that don't just report data but interpret it. A traffic management system might soon predict jams before they form, adjusting signal patterns dynamically. This shift from monitoring to anticipation represents the next evolution of smart cities.
Rethinking Municipal Operations
IoT is forcing cities to reevaluate traditional service models. Why collect garbage on a fixed schedule when sensors show exactly which bins need emptying? Why allocate parking enforcement officers evenly when data reveals violation hotspots? Resource allocation is moving from educated guesses to precise calculations.
Los Angeles' integrated transportation dashboard exemplifies this shift, combining data from buses, traffic signals, and ride-sharing apps to optimize the entire mobility network. The result? A 12% reduction in average commute times despite population growth. IoT enables cities to do more with existing resources, a crucial advantage in budget-conscious times.
Sustainable Resource Management through IoT Integration
Precision in Public Utilities
Chicago's water department saved $10 million annually by installing acoustic sensors that detect leaks in underground pipes. Similar systems now monitor electricity grids, identifying inefficiencies invisible to human inspectors. These technologies transform utilities from blunt instruments to surgical tools, conserving resources while maintaining service quality.
The impact extends beyond cost savings. In Cape Town, IoT-enabled water management helped avert Day Zero during their recent drought. Smart meters provided granular consumption data, allowing targeted conservation measures. When resources are scarce, IoT provides the visibility needed for equitable distribution.
Predictive Maintenance Revolution
New York's subway system now uses vibration sensors to identify track anomalies before they cause delays. This approach—applied to everything from sewer lines to streetlights—shifts maintenance from reactive to proactive. Cities save money by fixing small problems before they become big ones, while residents enjoy more reliable services.
Amsterdam's bridge monitoring system illustrates the potential. Sensors track structural stress, temperature fluctuations, and corrosion rates. Algorithms predict maintenance needs with 94% accuracy, allowing repairs during off-peak hours. This predictive approach minimizes disruptions while maximizing infrastructure lifespan.
Waste Not, Want Not
Seoul's smart waste management reduced collection costs by 83% using fill-level sensors and optimized routes. The system accounts for factors like weather and local events, adjusting schedules dynamically. Such efficiency gains make environmental sustainability financially sustainable, removing the traditional trade-off between green initiatives and budgets.
Portland takes this further with smart composting programs. Sensors in food waste bins track participation rates and contamination levels, guiding education campaigns. The result? A 34% increase in proper composting with cleaner, more valuable end product. IoT turns waste streams into feedback loops for continuous improvement.
Engaging Citizens as Partners
Boston's Street Bump app transforms smartphones into pavement sensors, crowdsourcing road condition data. This approach—applied to everything from air quality to noise pollution—turns residents into active participants in urban management. The data benefits city planners while fostering civic engagement.
Tokyo's energy challenge program takes citizen participation further. Real-time household consumption data, presented through gamified interfaces, reduced peak demand by 11%. When people see their impact, they become invested in solutions, creating a virtuous cycle of awareness and action.
Data-Driven Governance
London's Data Store makes thousands of IoT datasets publicly available, fueling innovation while ensuring transparency. This openness allows researchers, businesses, and citizens to find novel applications for municipal data. The most impactful IoT applications often come from unexpected sources, like a university student using traffic data to optimize bus routes.
Such platforms require careful privacy safeguards. Barcelona's Decidim platform shows how to balance openness with protection, using anonymization techniques while maintaining data utility. The future belongs to cities that harness collective intelligence without compromising individual rights.
Migraines are debilitating headaches often characterized by throbbing pain, typically affecting one side of the head. These episodes frequently bring nausea, light sensitivity, and sound intolerance. Recognizing personal triggers forms the foundation of effective migraine management. Common precipitants include stress fluctuations, sleep pattern changes, specific foods, weather shifts, and strong odors. Understanding these triggers enables proactive measures to potentially reduce attack frequency and severity. Relief strategies span from medication to relaxation techniques, while lifestyle adjustments like sleep regulation and stress management often prove highly preventive.
Future Trends and Challenges in IoT-Enabled Smart Cities
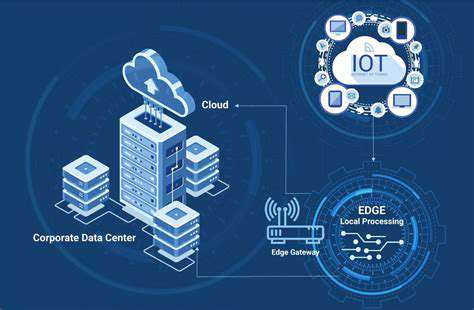
The Edge Computing Advantage
Seoul's pilot edge city project processes 90% of traffic camera data locally, reducing bandwidth needs while improving response times. This decentralized approach makes IoT systems more resilient and responsive, crucial for applications like emergency vehicle routing or crowd management during events.
Security in the Smart City Era
When Denver's traffic management system suffered a ransomware attack, it highlighted vulnerabilities in connected infrastructure. The city responded with blockchain-based authentication for all IoT devices. As cities grow smarter, cybersecurity must become as fundamental as pavement quality, built into every layer of urban planning.
Making Data Work Harder
Hong Kong's integrated operations center analyzes data from 35 municipal systems simultaneously, identifying correlations humans might miss. The real power emerges when diverse datasets converse, like correlating weather patterns with pothole formation or restaurant inspections with rodent sightings.
The Standardization Imperative
Toronto's troubled Sidewalk Labs experiment demonstrated the pitfalls of proprietary systems. The city now insists on open standards for all municipal IoT deployments. Interoperability isn't just technical—it's about maintaining civic control over essential services.
AI's Urban Renaissance
Singapore's Virtual Singapore project creates a digital twin of the entire city, simulating everything from flood risks to disease spread. These AI-powered models allow cities to stress-test decisions before implementation, potentially saving millions in misguided projects.
Privacy in Public Spaces
Amsterdam's TAPAS program gives citizens granular control over what personal data IoT systems collect. Finding the sweet spot between utility and privacy remains IoT's greatest challenge, requiring ongoing public dialogue and adaptable policies.
Industry Transformations
Oslo's electric vehicle infrastructure—integrated with renewable energy grids and parking sensors—shows how IoT can redefine entire sectors. The cities thriving tomorrow are those reimagining services today, using technology to meet changing needs sustainably.