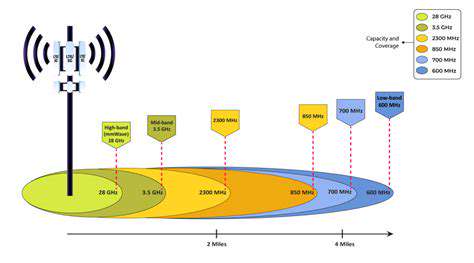
Addressing the Potential for Job Displacement and Economic Inequality
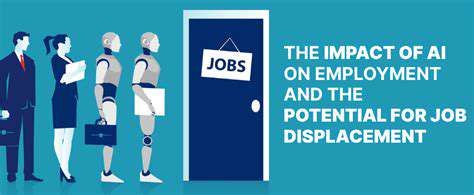
Addressing the Potential for Job Displacement
The increasing automation of tasks, driven by advancements in artificial intelligence and robotics, presents a significant challenge to the future of work. Many jobs currently performed by humans are at risk of being automated, leading to potential job displacement on a large scale. This raises concerns about the economic and social impacts, particularly for workers in industries heavily reliant on routine tasks. Understanding these potential impacts is crucial for developing strategies to mitigate the negative consequences and create opportunities for a more resilient workforce.
The transition to a more automated economy requires careful consideration of the skills needed in the future. Identifying and nurturing the skills that will be most in demand in an automated world is essential for ensuring that the workforce remains adaptable and competitive. This includes developing strategies for reskilling and upskilling existing workers, as well as preparing future generations for the evolving job market.
Impact on Different Sectors
Industries heavily reliant on manual labor, such as manufacturing and logistics, are particularly vulnerable to automation. Technological advancements have the potential to significantly alter the job landscape within these sectors, requiring workers to adapt to new roles and responsibilities. The impact on these industries extends beyond the immediate workforce, potentially affecting supply chains and economic structures.
The service sector, which encompasses a wide range of jobs, is also facing challenges due to automation. From customer service representatives to food preparation, automation has the potential to streamline processes and reduce costs. However, this may also lead to job displacement in these sectors, creating a need for workforce retraining and adaptation.
Strategies for Mitigation
Government policies play a crucial role in mitigating the potential negative impacts of job displacement. Investing in education and training programs that equip workers with the skills needed for the future job market is essential. These programs should focus on developing critical thinking, problem-solving, and creativity, skills that are less susceptible to automation.
Furthermore, policies that support entrepreneurship and small business creation can provide alternative employment opportunities. This can help to absorb some of the displaced workers and foster innovation within the economy. These approaches, along with fostering a supportive and adaptive environment, are key to ensuring a smooth transition to a future shaped by automation.
Reskilling and Upskilling Initiatives
Reskilling initiatives are crucial for helping workers transition to new roles in an automated economy. These initiatives should focus on providing training and development opportunities that equip workers with the skills needed for in-demand jobs. Providing accessible and affordable training programs, tailored to the needs of different industries, is vital. This includes offering courses in areas such as data analysis, artificial intelligence, and software development.
Upskilling programs are equally important for enhancing the skills of existing workers. These programs should focus on upgrading existing skills and knowledge to meet the demands of the changing job market. This could involve providing opportunities for workers to take advanced courses, participate in workshops, or obtain certifications in emerging fields. By investing in reskilling and upskilling initiatives, we can help workers adapt to the changing job market and maintain their economic security.
Social Safety Nets and Support Systems
In addition to reskilling and upskilling initiatives, robust social safety nets and support systems are necessary to protect workers during the transition to an automated economy. These systems should provide financial assistance, job placement services, and other resources to help displaced workers navigate the transition. This includes unemployment benefits, job search assistance, and access to affordable healthcare. It is essential to provide comprehensive support systems to ensure a smooth and equitable transition for all affected individuals.
Supporting workers through this transition requires a multifaceted approach that combines individual and systemic interventions. Providing access to resources and support during periods of job loss and retraining can significantly alleviate the stress and anxiety associated with this transition. A strong and supportive social safety net plays a critical role in ensuring that everyone has the opportunity to adapt and thrive in the changing job market.