Introduction to AI in Government
Introduction to AI in Government
Artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming various sectors, and government services are no exception. AI's ability to process vast amounts of data, identify patterns, and automate tasks offers significant potential to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance citizen engagement. From streamlining administrative processes to predicting and preventing crises, AI is becoming an increasingly important tool for modern governance.
This introduction will explore the core concepts of AI in government, highlighting its potential applications and the challenges associated with its implementation. Understanding these aspects is crucial for navigating the evolving landscape of public service delivery and harnessing AI's capabilities to create a more responsive and effective government.
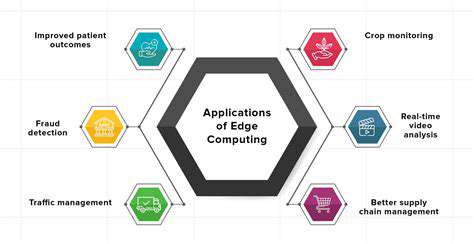
Improving Efficiency in Public Services
One of the most significant benefits of AI in government is its potential to streamline public services. AI-powered systems can automate routine tasks, freeing up human resources to focus on more complex and strategic initiatives. This automation can lead to faster processing times for applications, reduced wait times for citizens, and improved overall efficiency in various government departments.
For example, AI can automate tasks like processing tax returns, issuing permits, and scheduling appointments, reducing the workload on human staff and potentially reducing errors.
Enhancing Citizen Engagement
AI can play a crucial role in enhancing citizen engagement by providing more personalized and accessible services. AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants can answer citizen queries, provide information about government services, and guide individuals through complex processes. This personalized approach can improve citizen satisfaction and foster a more collaborative relationship between the government and its constituents.
Predictive Modeling for Public Safety
AI algorithms can analyze vast datasets to identify patterns and predict potential risks and crises. For instance, AI can analyze crime data to predict crime hotspots, allowing law enforcement agencies to deploy resources proactively and potentially reduce crime rates. Similarly, AI can predict potential natural disasters, enabling governments to prepare for and mitigate their impact.
Data Security and Privacy Concerns
Implementing AI in government raises critical data security and privacy concerns. Protecting sensitive citizen information is paramount. Robust security measures, transparent data governance policies, and adherence to privacy regulations are essential to ensure public trust and prevent misuse of AI systems.
Ethical Considerations and Bias Mitigation
AI systems can inherit biases present in the data they are trained on, potentially leading to discriminatory outcomes. This necessitates careful consideration of ethical implications and the development of strategies to mitigate bias. Regular audits and evaluations of AI systems are crucial to ensure fairness and equity in their application to government services. Addressing these ethical concerns proactively is essential for building trust and ensuring responsible AI implementation.
The Future of AI in Government
The future of AI in government is promising, with ongoing advancements in AI technology continually expanding its potential applications. As AI systems become more sophisticated and accessible, governments can leverage them to address complex societal challenges, improve public services, and enhance citizen experiences. However, careful planning, ethical considerations, and robust safeguards are essential to ensure responsible and equitable implementation of AI in government services.

Future Trends and Challenges in Implementing AI
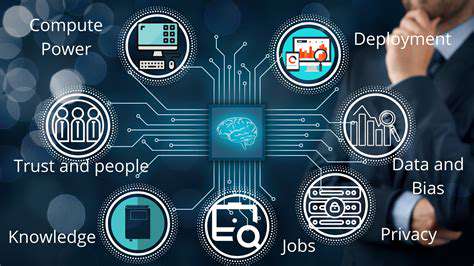
Emerging Technologies
The integration of cutting-edge technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) is poised to revolutionize the field of immersive experiences. AI-powered personalization will create highly tailored and engaging environments for individual users, significantly enhancing immersion and user satisfaction. This personalization extends beyond content selection, potentially adapting the very physical and virtual spaces to the user's emotional state and preferences in real-time. These advancements promise to create more deeply engaging and emotionally resonant experiences than ever before.
Furthermore, advancements in virtual and augmented reality (VR/AR) hardware are creating more accessible and affordable opportunities for immersive experiences. The development of more comfortable and intuitive VR headsets and AR overlays will broaden the reach of these technologies, making them more accessible to a wider range of users. This increased accessibility, coupled with decreasing hardware costs, is expected to drive widespread adoption and innovation across various industries, from entertainment and education to healthcare and training.
Accessibility and Inclusivity
A key challenge in the future of immersive technologies lies in ensuring accessibility and inclusivity. Current immersive experiences often exclude users with disabilities, limiting their ability to fully participate. Future development must prioritize the creation of experiences that are accessible to individuals with a wide range of physical, cognitive, and sensory needs. This involves considering diverse user inputs, including alternative control methods and adaptive interfaces, to cater to different requirements.
Furthermore, ensuring equitable access to resources and opportunities for diverse communities is crucial. The cost of developing and deploying immersive experiences, coupled with potential digital divides, can exacerbate existing inequalities. Strategies for affordability and widespread access, such as subsidized development programs and community-based initiatives, are necessary to foster inclusivity and ensure that immersive technologies benefit all members of society.
Economic and Societal Implications
The widespread adoption of immersive technologies will inevitably have profound economic and societal implications. New industries and job markets will emerge, requiring specialized skills and training in areas like immersive content creation, design, and development. The potential for economic disruption, as well as the opportunities for growth, need careful consideration and proactive strategies for workforce development. Governments and educational institutions must work together to equip individuals with the necessary skills to thrive in this evolving landscape.
Ethical considerations surrounding user privacy, data security, and potential misuse of immersive technologies are paramount. Establishing clear guidelines and regulations to address these concerns is critical to ensure responsible innovation and prevent unintended consequences. Open dialogues and collaboration between technologists, policymakers, and the public are necessary to navigate these complex issues and ensure that immersive technologies are used ethically and beneficially.