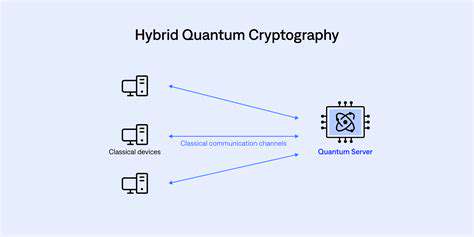
Quantum Key Distribution (QKD)
Quantum key distribution (QKD) is a revolutionary cryptographic technique that leverages the principles of quantum mechanics to create a shared secret key between two parties. This key can then be used to encrypt and decrypt messages, ensuring their confidentiality and integrity. Unlike traditional cryptography, QKD offers a provably secure method of key exchange, as any attempt to intercept the key will inevitably disturb the quantum state, alerting the legitimate parties to the intrusion. This fundamental security guarantee is a crucial advantage in today's increasingly complex security landscape. Quantum mechanics dictates that observing a quantum system inevitably alters its state, making eavesdropping detectable.
The core principle behind QKD is the use of quantum phenomena, such as the superposition and entanglement of photons, to transmit information. This allows for the generation of a secret key that is inherently secure. This is a significant departure from traditional cryptographic methods, which rely on mathematical assumptions that could potentially be proven false. The inherent security of QKD stems from the fundamental laws of quantum mechanics, ensuring that any attempt to intercept the key will be detectable.
Security Advantages
Quantum cryptography offers unparalleled security, as the very act of eavesdropping disturbs the quantum state. This disturbance is immediately detectable by the communicating parties, ensuring the integrity of the shared key. Unlike classical cryptography, which relies on the computational difficulty of solving certain mathematical problems, QKD's security is rooted in the fundamental laws of physics. This makes it impervious to advances in computing power and the development of increasingly sophisticated algorithms.
Practical Applications
Quantum cryptography has a wide range of practical applications, including secure communication channels for financial transactions, government communications, and sensitive data transmission. Its potential to enhance security in critical infrastructure and sensitive data handling makes it a highly sought-after technology. In the future, quantum cryptography may also play a crucial role in securing global communication networks and protecting sensitive data in cloud storage systems.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite its inherent security advantages, quantum cryptography faces several challenges, including the need for specialized quantum communication equipment and the limited distances over which quantum signals can be transmitted reliably. However, ongoing research and development efforts are addressing these challenges. Researchers are actively exploring new technologies and materials to improve the efficiency and range of quantum communication systems. This ongoing research promises to unlock the full potential of quantum cryptography in the near future, paving the way for a more secure and trustworthy digital world.
Technological Advancements
Significant advancements in quantum technologies are continuously pushing the boundaries of quantum cryptography. This includes improvements in quantum key distribution protocols, development of more robust quantum communication channels, and refinement of quantum sensors for eavesdropping detection. These advancements are leading to more efficient and practical implementations of QKD in various real-world scenarios. Furthermore, the integration of quantum cryptography into existing communication infrastructure is a crucial step towards its broader adoption. As technology continues to evolve, quantum cryptography has the potential to revolutionize secure communication in the years to come.
Key Distribution via Quantum Entanglement: The Essence of Quantum Cryptography
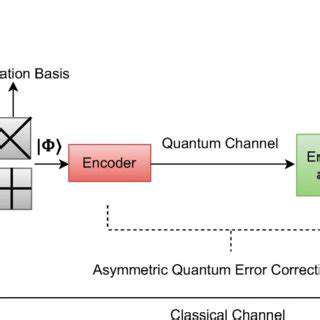
Quantum Key Distribution: A Secure Foundation
Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) leverages the principles of quantum mechanics to create a fundamentally secure method for sharing cryptographic keys. Unlike traditional methods, QKD's security is intrinsically linked to the laws of physics, making it resistant to eavesdropping attacks that are impossible to detect with classical cryptography. This inherent security stems from the fact that any attempt to intercept the quantum signals used to generate the key immediately alters the quantum state, alerting the legitimate users.
The Role of Entanglement in QKD
Entanglement is a crucial element in QKD protocols. Quantum entanglement creates a profound correlation between two or more particles, regardless of the distance separating them. If two entangled particles are measured, their outcomes are correlated in a predictable way. This correlation is exploited in QKD to generate a shared secret key. This fundamental property of quantum mechanics forms the basis of QKD's unbreakable security. The measurement of the entangled particles' states determines the shared key.
Security Against Eavesdropping Attacks
QKD's security is built on the impossibility of perfectly copying quantum states, a concept known as the No-Cloning Theorem. Any attempt by an eavesdropper to intercept and measure the quantum signals used to generate the key inevitably alters the quantum state. This alteration is detectable by the legitimate users, immediately breaking the communication and alerting them to the presence of an eavesdropper. This inherent vulnerability of quantum systems to eavesdropping makes QKD a truly unbreakable system for secure communication.
Practical Implementation and Challenges
Implementing QKD systems presents some practical challenges. One significant hurdle is the need for specialized quantum hardware, which can be expensive and complex. The transmission of quantum signals over long distances is also problematic due to signal loss and decoherence. However, ongoing research and development are actively addressing these challenges. Continued innovation in quantum technologies promises to make QKD more accessible and practical for widespread use in the future.
Future Applications and Potential
The potential applications of QKD extend far beyond secure communication channels. It has the potential to revolutionize financial transactions, secure sensitive data transmission, and enhance the security of critical infrastructure. Further advancements in the field are expected to lead to more robust and reliable systems capable of addressing the demands of future communication needs. With ongoing research and development, QKD is poised to become an essential component of future secure communication networks. It could significantly strengthen the security of online transactions and government communications.
Practical Applications and Future Outlook

Real-World Implementations
Numerous practical applications are already leveraging the power of advanced AI. From personalized recommendations on e-commerce platforms to automated customer service chatbots, AI is transforming how businesses operate and interact with consumers. These applications demonstrate the potential for AI to streamline processes, reduce costs, and enhance user experiences. This integration into existing systems showcases the ease of implementation and the significant improvements it can bring.
In healthcare, AI algorithms are being utilized to analyze medical images, aiding in faster and more accurate diagnoses. This not only improves patient outcomes but also has the potential to reduce healthcare costs by identifying potential issues early on. Further advancement in this area promises to revolutionize the way medical professionals approach patient care. The potential benefits are immense, and the development and deployment of these applications are constantly evolving.
Emerging Trends and Opportunities
The future of AI holds exciting possibilities, with emerging trends like the development of sophisticated AI assistants, automated decision-making systems, and the integration of AI into various sectors. This evolution is driving innovation in areas ranging from transportation to manufacturing, promising significant improvements in efficiency and productivity.
One particularly promising area is the development of AI-powered tools for personalized learning. These systems can adapt to individual learning styles and paces, providing tailored educational experiences that cater to the specific needs of each student. This approach can significantly improve educational outcomes and foster a deeper understanding of complex subjects. This tailored approach has the potential to revolutionize education as we know it.
Furthermore, the integration of AI into various industries is creating new job opportunities and demanding new skill sets. This presents a unique opportunity for individuals to adapt and acquire the necessary skills to thrive in this evolving landscape. The future is shaping up to be a time of both challenge and opportunity for individuals and businesses alike. The ability to adapt to this technological advancement will be a key factor in success.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
Despite the numerous benefits, the widespread adoption of AI presents certain challenges. Ensuring the fairness and transparency of AI algorithms is crucial to prevent bias and ensure equitable outcomes. Robust regulatory frameworks are needed to address these issues and ensure ethical use of AI technology. The ethical implications of AI are complex and require careful consideration.
Another challenge lies in the potential for job displacement due to automation. Addressing this concern requires proactive measures to reskill and upskill the workforce to adapt to the changing job market. The transition to an AI-driven economy necessitates careful planning and foresight to mitigate potential negative impacts. This involves fostering a learning environment that allows individuals to adapt and embrace new technologies.
Finally, the security of AI systems is paramount. Protecting sensitive data and preventing malicious use of AI technology requires robust security measures and ongoing research. Protecting this data from malicious actors is essential for ensuring the safety and integrity of AI systems. The need for security measures will be a constant concern in this quickly evolving field. This necessitates a multi-faceted approach from the development stage to the implementation stage.