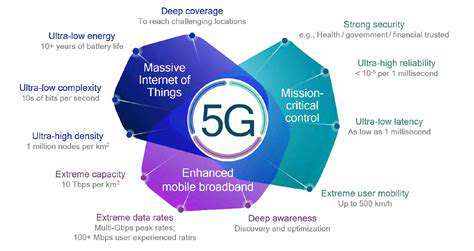
Understanding the Different 5G Frequency Bands
5G technology relies on a range of radio frequencies, often referred to as bands, to transmit data. These bands operate at different frequencies, each with its own set of characteristics, impacting factors such as range, speed, and signal penetration. Different bands are optimized for different use cases, reflecting the diverse needs of 5G applications. Understanding these frequency bands is crucial for comprehending the intricacies of 5G deployment and its potential applications.
The spectrum allocated for 5G is not a single, monolithic block but rather a collection of frequencies, each with unique attributes. This spectrum encompasses a wide range, from lower frequencies, which often have better penetration through obstacles, to higher frequencies, known for their potential for higher data rates. The specific allocation of these frequencies varies across countries, influenced by regulatory and technological considerations.
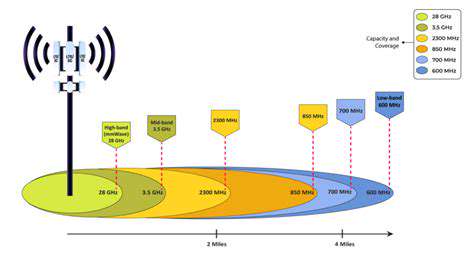
Low-Band 5G: The Long-Range Performer
Low-band 5G frequencies, typically operating below 1 GHz, offer extended range and excellent penetration. This characteristic makes them ideal for connecting large areas, such as rural communities, with reliable coverage. Low-band signals generally travel further, passing through buildings and foliage with less signal degradation, leading to broader network coverage. This feature is especially advantageous for applications requiring broad reach, like smart city deployments and mass market connectivity.
However, low-band 5G often comes with lower data rates compared to higher-band frequencies, so it's not suited for applications that demand extremely high speeds. This tradeoff between range and speed is a key consideration in 5G deployment planning, balancing the need for broad coverage with the demand for faster speeds.
Mid-Band 5G: A Balanced Approach
Mid-band 5G frequencies, generally between 3 GHz and 6 GHz, offer a balance between range and speed. They provide a good compromise between the extensive coverage of low bands and the high speeds achievable with higher frequencies. Mid-band 5G is well-suited for a broad range of applications, including mobile internet access, video streaming, and other data-intensive activities. These frequencies typically have a good balance of range and speed, making them a versatile choice for various applications.
Deployments in urban areas often favor mid-band frequencies due to their ability to provide high data rates without sacrificing substantial reach. This makes it a prominent choice for dense populations and high-traffic areas.
High-Band 5G: The Speed Demon
High-band 5G frequencies, operating above 24 GHz, offer exceptionally high data rates, enabling ultra-fast speeds for demanding applications like gaming, video conferencing, and virtual reality. The high frequencies allow for a substantial amount of data transmission, making it suitable for applications that require high bandwidth.
However, high-band 5G signals are more susceptible to obstacles and have a shorter range compared to lower bands. This means that high-band deployments often require a denser network of base stations to maintain consistent coverage, which can be more complex and costly than low-band deployments. This requires careful consideration of deployment strategies to ensure reliable coverage.
Spectrum Allocation and Regulatory Considerations
The allocation of 5G spectrum is a crucial aspect of deploying the technology. Different countries adopt various strategies for assigning frequencies, reflecting specific technological needs and regulatory frameworks. This process often involves careful coordination and negotiation to ensure efficient use of the spectrum and to avoid interference with existing wireless services.
Regulatory bodies play a vital role in overseeing the spectrum allocation process. Their decisions influence the development and adoption of 5G technologies, ensuring that the technology is deployed in a way that meets the needs of the country while minimizing interference with existing wireless services.
The Impact of Spectrum on 5G Performance
The choice of spectrum significantly influences the performance characteristics of a 5G network. Factors like coverage, speed, and latency are directly affected by the frequency band utilized. Understanding the specific properties of each band is essential for optimizing network design and ensuring that 5G meets the diverse needs of users across different environments.
Choosing the right frequency band for a particular application or location is a critical aspect of 5G deployment. A well-planned spectrum strategy enables operators to build robust and efficient networks capable of supporting the demands of modern communication.
Anxiety, a pervasive emotional state characterized by worry, fear, and unease, often manifests in various physical symptoms. Nausea, a feeling of discomfort in the stomach often leading to the urge to vomit, is a common physical manifestation of anxiety. This connection lies in the intricate interplay between the brain and the autonomic nervous system. The sympathetic nervous system, activated during anxiety, can trigger a cascade of physiological responses, including increased heart rate, rapid breathing, and, crucially, altered gastrointestinal function. This can lead to the sensations of nausea, sometimes accompanied by other digestive issues like stomach cramps and indigestion.