Quantum Cryptography for Enhanced Security
Quantum Cryptography: A New Era of Security
This emerging field applies quantum mechanical principles to establish theoretically unbreakable encryption, representing a fundamental security upgrade over conventional methods. Quantum cryptography's robustness originates from physical laws rather than mathematical complexity, ensuring protection against even future quantum attacks.
Quantum phenomena like entanglement enable creation of inherently secure cryptographic keys. Any interception attempt unavoidably alters quantum states, immediately revealing eavesdropping attempts. This self-monitoring characteristic forms the foundation of quantum cryptography's unparalleled security guarantees.
Protecting Financial Data with Quantum Cryptography
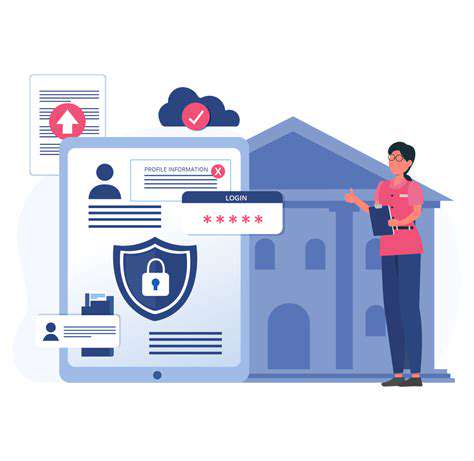
Financial institutions handling sensitive transactional data stand to benefit significantly from quantum cryptographic solutions. Adoption could ensure bulletproof security for customer information and financial transactions.
Implementation may establish a new standard for financial security where digital transactions become virtually impervious to compromise. Such advancements could dramatically increase public trust in electronic banking systems.
Quantum Key Distribution (QKD): A Practical Approach
QKD enables secure key exchange between parties, with the generated keys used alongside traditional encryption. As QKD systems mature, they're becoming more viable for real-world deployment in sectors like finance.
Overcoming Challenges in Implementation
While theoretically secure, practical quantum cryptography faces hurdles including high implementation costs and technical limitations in long-distance transmission. Research focuses on improving system affordability and reliability for broader adoption.
Future Applications and Implications
Beyond finance, quantum cryptography could transform security in healthcare, government, and defense sectors. Widespread adoption might fundamentally alter digital security paradigms across multiple industries. Though challenges remain, the technology's transformative potential is clear.
Challenges and Future Outlook

Navigating Economic Uncertainty
The current volatile economic environment creates significant obstacles for businesses. Organizations must develop adaptable strategies to manage risks from fluctuating markets and geopolitical instability. Building operational flexibility is essential for enduring unpredictable economic conditions.
Technological Advancements and Disruptions
Accelerating technological innovation presents both opportunities and challenges. Companies must continuously evolve to integrate emerging technologies like AI and IoT or risk competitive disadvantage. Successful adoption requires substantial investment in workforce training and infrastructure.
Sustainability and Environmental Concerns
Environmental regulations and consumer expectations are driving businesses toward sustainable practices. Ecological responsibility has transitioned from optional to mandatory for long-term viability. Companies demonstrating genuine commitment to sustainability often gain marketplace advantages.
Talent Acquisition and Retention
The intensifying competition for skilled professionals requires innovative workforce strategies. Effective talent management now demands comprehensive approaches addressing compensation, development, and workplace culture. Companies must continually adapt their HR practices to attract and retain top performers.