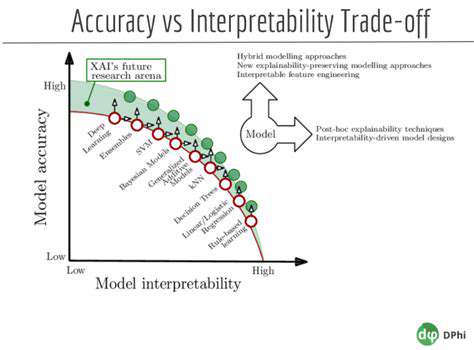
Why Early Detection Matters
Identifying health issues at their onset transforms treatment possibilities. Catching diseases early frequently means simpler, more effective interventions that can halt progression before severe complications arise. This approach doesn't just improve survival rates - it preserves quality of life by minimizing invasive procedures.
Beyond medical benefits, early diagnosis gives patients agency over their health journey. When people understand their condition sooner, they can implement dietary changes, adjust medications, and modify behaviors with greater impact. This knowledge becomes particularly powerful for chronic conditions where lifestyle plays a major role.
Preventive Healthcare Strategies
Consistent medical evaluations form the foundation of preventive care. These routine visits uncover silent health threats through comprehensive screenings and expert assessment - often before patients notice any warning signs. Blood panels, imaging studies, and specialized tests work together to create a complete health snapshot.
Modern diagnostic tools now detect microscopic cellular changes and subtle biochemical shifts. Such precision allows for interventions when they're most effective - sometimes even reversing early disease processes through targeted therapies and lifestyle modifications.
Screening Protocols That Save Lives
Population-specific screening programs represent one of medicine's greatest preventive achievements. Customized testing regimens based on age, genetics, and risk factors catch approximately 30% of cancers at treatable stages. Mammography programs demonstrate this perfectly, with regular participants showing 40% lower breast cancer mortality.
Innovative screening continues to evolve - liquid biopsies now identify tumor DNA in blood samples, while advanced imaging detects cardiovascular risks years before symptoms emerge. These technologies create unprecedented opportunities for preemptive healthcare strategies.
Lifestyle as Preventive Medicine
Daily choices accumulate into powerful health determinants. Nutrition, activity levels, and stress management don't just prevent disease - they actively promote cellular repair mechanisms. The Mediterranean diet, for instance, shows measurable impacts on inflammatory markers and cardiovascular health metrics.
Behavioral modifications achieve what medications cannot - addressing root causes rather than symptoms. Smoking cessation reverses lung damage, while regular exercise regulates blood sugar as effectively as many pharmaceuticals. These interventions gain even greater importance when implemented early.
Diagnostic Technology Revolution
Modern imaging provides extraordinary insights into human physiology. High-resolution scanners now visualize microcalcifications in breast tissue and early arthritic changes invisible to conventional X-rays. Coupled with AI analysis, these tools detect patterns even experienced radiologists might miss.
Genomic testing represents another frontier, identifying predisposition markers decades before disease manifestation. This predictive capability enables truly personalized prevention plans based on individual biological risks rather than population averages.
Empowered Healthcare Consumers
Informed patients drive better outcomes through proactive engagement. Health literacy directly correlates with earlier diagnosis rates across multiple conditions, as knowledgeable individuals recognize subtle warning signs and seek timely evaluation.
Educational initiatives that demystify medical concepts create populations better equipped to partner with healthcare providers. This collaborative approach yields more accurate histories, better compliance, and ultimately, superior clinical results through shared decision-making processes.
Transformative Diagnostic Advancements
Precision Diagnostics Through AI
Advanced imaging analytics now detect pathological changes with superhuman consistency. Machine learning models trained on millions of cases identify microstructural abnormalities and quantify disease progression markers with 0.1mm precision. This capability proves particularly valuable in neurological conditions where early cellular changes precede symptoms by years.
Multimodal analysis synthesizes data from disparate sources - combining functional MRI readings with perfusion scans and laboratory values to create comprehensive disease profiles. This systems biology approach moves diagnosis beyond isolated findings to interconnected physiological understanding.
Personalized Treatment Design
Therapeutic planning achieves new sophistication through computational modeling. Radiation oncology now utilizes AI-driven dose optimization that accounts for tumor geometry, surrounding tissue radiosensitivity, and predicted cellular response patterns. Such precision reduces collateral damage while increasing target effectiveness.
Surgical simulations leverage patient-specific 3D reconstructions to rehearse complex procedures virtually. Surgeons can test multiple approaches, measure predicted blood loss, and identify anatomical variations before making the first incision. This preparation translates to shorter OR times and improved recovery metrics.
Streamlined Clinical Workflows
Automated analysis tools slash interpretation times for routine studies by 60-80%, allowing specialists to focus on complex cases requiring human judgment. Emergency departments particularly benefit from accelerated stroke and trauma evaluations where minutes impact outcomes.
Standardized reporting templates ensure consistent communication across care teams while reducing documentation burdens. Natural language generation creates preliminary reports that clinicians can quickly verify and augment with clinical context, maintaining accuracy while improving efficiency.
Optimized Healthcare Delivery
Resource allocation achieves new precision through predictive analytics. Imaging utilization algorithms help prioritize studies based on clinical urgency and predicted diagnostic yield, reducing unnecessary procedures. This intelligent triaging improves access for patients with genuine need while controlling costs.
Overcoming Implementation Hurdles
Data Quality Imperatives
Developing robust AI models requires overcoming significant data challenges. Curating representative datasets that include rare conditions and demographic variations demands international collaboration across institutions. Annotation protocols must balance expert verification with scalability to handle the petabytes of imaging data generated annually.
Privacy-preserving techniques like federated learning enable model training without centralized data aggregation. Differential privacy methods add mathematical safeguards that prevent re-identification while maintaining analytical utility, addressing legitimate confidentiality concerns.
Transparent Decision Making
Next-generation diagnostic AI incorporates explainability by design. Attention maps highlight relevant image regions influencing conclusions, while confidence intervals quantify prediction certainty. This transparency builds clinician trust and facilitates appropriate reliance on algorithmic assistance.
Equitable Algorithm Development
Bias mitigation begins with diverse training cohorts representing all populations served. Continuous monitoring for performance disparities across demographic groups ensures equitable care quality. Technical solutions include adversarial debiasing during model training and stratified performance validation.
Clinical Integration Strategies
Successful implementation requires workflow-aware system design. Embedded decision support that appears at natural workflow pause points receives higher utilization than separate applications. Context-aware interfaces adapt to specialty-specific needs, whether prioritizing speed for emergency reads or detailed analysis for oncologic staging.
Regulatory Frameworks
Evolving certification processes balance innovation with patient safety. Adaptive regulations accommodate continuous learning systems while maintaining rigorous validation standards. Liability frameworks increasingly recognize AI as a clinical tool rather than replacement for physician judgment, with appropriate accountability structures.