AI-Powered Disease Surveillance and Outbreak Detection
Early Detection and Prevention Strategies
AI-powered disease surveillance systems offer a powerful tool for early detection of outbreaks, allowing for rapid response and prevention strategies. These systems can analyze vast amounts of data, identifying patterns and anomalies that might otherwise go unnoticed by human analysts. This early detection is crucial for containing the spread of infectious diseases and mitigating their impact on public health.
By proactively identifying potential outbreaks, health authorities can implement targeted interventions, such as contact tracing and quarantine measures, to prevent further transmission. This proactive approach can significantly reduce the severity and duration of disease outbreaks.
Data Integration and Analysis Capabilities
A key strength of AI in disease surveillance is its ability to integrate and analyze diverse data sources, such as patient records, social media posts, and environmental data. This comprehensive approach allows for a more nuanced understanding of disease trends and potential risk factors. For instance, AI algorithms can identify correlations between environmental conditions and disease outbreaks, providing valuable insights for public health interventions.
Combining different data streams can lead to a more complete picture of the situation, allowing for the development of more effective and targeted interventions. This holistic approach is crucial for understanding the complex interplay of factors that contribute to disease outbreaks.
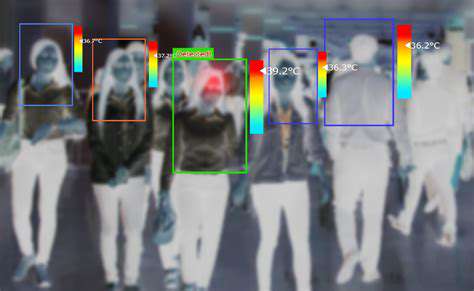
Real-Time Monitoring and Alerting
AI systems excel at real-time monitoring of disease trends, enabling rapid identification of potential outbreaks. This real-time capability is critical for minimizing the time it takes to respond to emerging health threats. By constantly analyzing data streams, AI algorithms can generate alerts when patterns indicative of an outbreak are detected, allowing for immediate intervention.
This quick response can significantly limit the spread of the disease. Early intervention measures can dramatically reduce the severity and scale of an outbreak.
Improved Accuracy and Efficiency
AI-powered systems significantly improve the accuracy and efficiency of disease surveillance compared to traditional methods. By automating data analysis and pattern recognition, AI algorithms can process vast quantities of data much faster than human analysts. This increased efficiency allows for timely identification of potential outbreaks, facilitating rapid responses and potentially saving lives.
Moreover, the increased accuracy of AI analysis reduces the likelihood of false positives or false negatives. This enhanced accuracy is essential for ensuring that public health resources are used effectively and efficiently.
Enhanced Public Health Preparedness
AI-powered disease surveillance systems contribute to enhanced public health preparedness. These systems provide valuable insights into disease trends and patterns, enabling the development of more effective prevention strategies. This proactive approach allows public health agencies to anticipate and prepare for future outbreaks, minimizing potential damage. By anticipating the needs of affected populations, preventive measures can be implemented and resource allocation can be optimized, reducing the overall impact of disease outbreaks.
Global Collaboration and Data Sharing
AI-powered disease surveillance can facilitate global collaboration and data sharing among different countries. This international cooperation is crucial for addressing global health threats. Sharing data and insights across borders allows for a more comprehensive understanding of disease patterns and facilitates the development of coordinated responses. This collaboration allows for a more effective exchange of information and knowledge, leading to more effective prevention and control strategies worldwide. International collaboration is vital in combating pandemics.
Ethical Considerations and Data Security
The implementation of AI-powered disease surveillance systems raises important ethical considerations. Data privacy and security must be paramount in the design and implementation of these systems. Careful consideration of data ownership, access, and usage is essential to ensure responsible data handling. Transparency and accountability are crucial to build public trust and confidence in these systems.
These systems must prioritize the privacy and security of individual health information. Protecting sensitive data is essential to maintain public trust and confidence in these systems.