Improving Diagnostic Accuracy
IoT-enabled diagnostics are transforming healthcare delivery through continuous physiological monitoring. The constant data stream allows clinicians to spot anomalies that traditional intermittent check-ups might miss. By combining inputs from multiple devices, providers gain a comprehensive, real-time picture of patient health.
Advanced analytics uncover subtle patterns invisible to human observation. This enhanced diagnostic precision leads to faster, more accurate interventions while reducing unnecessary invasive procedures.
Remote Patient Monitoring
For chronic conditions, IoT monitoring represents a breakthrough. Continuous home monitoring dramatically reduces hospital visits while improving quality of life. Patients enjoy greater independence while clinicians receive richer datasets for decision-making.
The psychological benefits are equally important. Empowered patients who understand their health metrics become more compliant with treatment regimens, leading to better long-term outcomes.
Enhanced Efficiency and Cost Savings
IoT integration streamlines healthcare operations significantly. Automated data collection reduces administrative burdens, freeing clinicians to focus on patient care rather than paperwork. These efficiency gains translate to substantial cost reductions across healthcare systems.
Optimized resource allocation becomes possible when routine monitoring happens automatically. This is particularly valuable in resource-constrained environments where healthcare access remains challenging.
Personalized Treatment Plans
The granular data from IoT devices enables truly personalized medicine. Treatment protocols can be fine-tuned to individual physiology, maximizing effectiveness while minimizing side effects. This represents a quantum leap beyond standardized treatment approaches.
Dosage adjustments, treatment duration, and complementary therapies can all be optimized based on continuous feedback from monitoring devices, creating dynamic treatment plans that evolve with patient needs.
Data Security and Privacy Concerns
While benefits abound, security remains paramount. Healthcare organizations must implement end-to-end encryption and strict access controls to protect sensitive patient data. Compliance with evolving privacy regulations requires ongoing vigilance and investment in cybersecurity infrastructure.
Clear patient communication about data usage policies builds essential trust. When patients understand how their information is protected and used, they're more likely to embrace these transformative technologies.
Precision Medicine and Personalized Treatment Plans
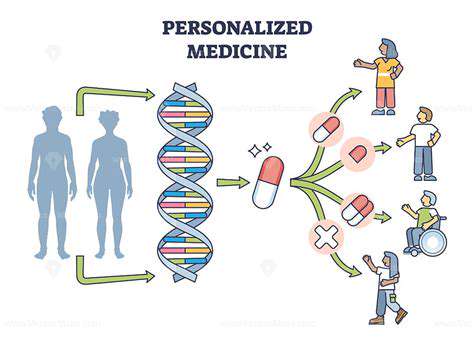
Precision Medicine: A Revolution in Healthcare
Precision medicine represents a fundamental shift from generalized treatments to customized care plans. By considering genetic, lifestyle, and environmental factors, this approach delivers superior outcomes with fewer side effects.
Personalized Genomics and Diagnostics
Genomic sequencing unlocks the blueprint of individual health predispositions. Identifying genetic markers enables early interventions that can prevent disease onset or progression. Advanced diagnostics now analyze multiple biomarkers simultaneously, creating comprehensive health profiles.
This multi-factorial analysis allows for precise disease subtyping, ensuring patients receive treatments specifically matched to their condition's unique characteristics.
Tailored Treatments and Therapies
Armed with detailed genetic and diagnostic information, clinicians can design treatment regimens optimized for each patient. These may include targeted biologics, gene therapies, or customized lifestyle modifications based on metabolic profiles.
Pharmacogenomics: A Personalized Approach to Drug Response
Understanding genetic influences on drug metabolism revolutionizes prescribing practices. Pharmacogenomic testing can predict medication effectiveness and adverse reaction risks before treatment begins. This prevents trial-and-error prescribing and its associated costs and complications.
Challenges and Considerations in Implementation
Despite its promise, precision medicine faces hurdles. The high cost of genomic testing creates access disparities that must be addressed. Ethical considerations around genetic data usage require robust governance frameworks to maintain public trust.
Interoperability between systems and standardized data formats are technical challenges that must be overcome for widespread adoption across healthcare networks.
Future Directions and Implications
The trajectory of precision medicine points toward increasingly sophisticated diagnostics and treatments. As our understanding of human biology deepens, we're moving toward predictive healthcare that prevents illness before symptoms appear. This paradigm shift will transform not just individual care, but entire public health strategies and healthcare economics.
Canine aggression arises from complex interactions between genetics, environment, and learned behaviors. Effective management requires identifying specific triggers through careful observation of body language and situational context. Dogs with traumatic histories may display defensive aggression that requires specialized behavioral interventions tailored to their individual experiences.