Improving Adherence and Patient Engagement Through AI
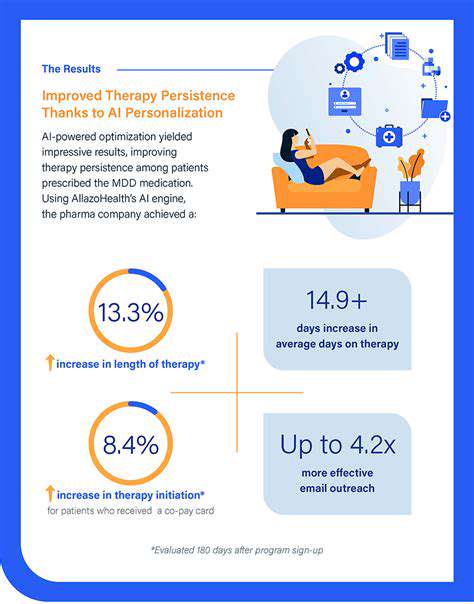
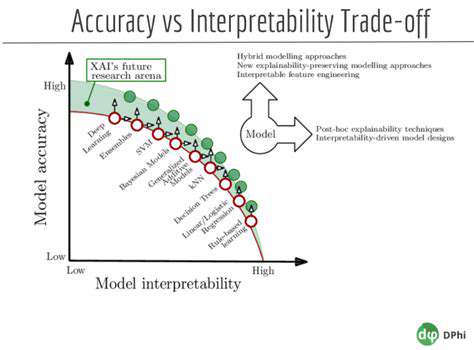
Improving Medication Adherence: A Multifaceted Approach
Medication adherence, the consistent taking of prescribed medications as directed by a healthcare professional, is crucial for effective treatment and positive health outcomes. Poor adherence significantly impacts patient well-being and can lead to complications, increased healthcare costs, and potentially, treatment failure. This underscores the critical need for strategies that support patients in achieving and maintaining adherence.
Factors influencing adherence are varied and complex, encompassing individual patient characteristics, socioeconomic conditions, and the characteristics of the medication itself. Understanding these factors is essential for developing targeted interventions.
Patient Education and Empowerment
Comprehensive patient education plays a pivotal role in fostering medication adherence. Educating patients about their condition, the purpose of their medication, potential side effects, and the importance of consistent dosing is vital. This empowers patients to actively participate in their treatment and make informed decisions.
Clear and concise communication, tailored to the patient's understanding and literacy level, is essential. Visual aids, written materials, and interactive sessions can significantly enhance comprehension.
Simplifying Medication Regimens
Complex medication regimens, with multiple doses and different times, can significantly hinder adherence. Streamlining medication schedules and potentially combining medications whenever possible can greatly improve patients' ability to manage their treatment effectively. By reducing the complexity of the regimen, patients are more likely to successfully integrate medication-taking into their daily lives.
For example, a doctor might prescribe a once-daily medication instead of multiple doses throughout the day. This simple change can have a huge impact on adherence.
Addressing Socioeconomic Factors
Socioeconomic factors, such as financial constraints, transportation issues, and access to healthcare resources, can significantly impact a patient's ability to adhere to their medication regimen. Addressing these barriers is critical to improving overall medication adherence rates.
Programs that provide financial assistance for medications, transportation support, and simplified access to healthcare facilities can mitigate these obstacles. Providing resources for these situations allows patients to focus on their health and treatment without added stress.
Utilizing Technology and Support Systems
Technological advancements offer numerous opportunities to enhance medication adherence. Mobile applications, reminders, and remote monitoring systems can effectively support patients in taking their medications as prescribed. These tools offer a practical way to enhance patient engagement and improve overall compliance.
Furthermore, support groups and counseling services can provide emotional and psychological support, which is crucial in helping patients manage the challenges of chronic conditions and medication adherence.
Healthcare Provider Collaboration and Communication
Strong communication and collaboration between healthcare providers, patients, and their families are essential for successful medication adherence. Regular follow-up appointments, open communication channels, and proactive discussions about treatment plans are crucial to identify any challenges or concerns early on. Open dialogues between doctors and patients about medication side effects and adherence strategies are vital.
Providers must actively listen to patient concerns and adapt treatment plans as needed. This collaborative approach ensures that patients feel supported and empowered throughout their treatment journey.
The Future of AI in Chronic Disease Management: Challenges and Opportunities
Personalized Treatment Plans
AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of patient data, including medical history, genetic information, lifestyle factors, and environmental exposures, to create highly personalized treatment plans. This personalized approach goes beyond a one-size-fits-all model, tailoring interventions to the unique needs and characteristics of each individual. By identifying specific risk factors and predicting potential responses to different therapies, AI can significantly improve treatment efficacy and reduce adverse effects.
The ability to predict disease progression and tailor interventions to individual patients is a critical advancement. This personalized approach will dramatically improve patient outcomes by proactively managing risk factors and adapting treatments as needed. The integration of AI in chronic disease management, therefore, will not only improve efficacy but also enhance patient experience.
Improved Disease Monitoring and Prediction
AI-powered wearable devices and remote monitoring systems can continuously track vital signs, activity levels, and other health parameters. This real-time data collection allows for early detection of potential complications and enables proactive interventions. Furthermore, AI can analyze these data streams to identify patterns and predict future disease progression, empowering both patients and healthcare providers to take preventative measures and adjust treatment plans accordingly. This predictive capability is transformative, enabling earlier interventions and potentially preventing exacerbations.
The continuous monitoring capabilities offered by AI are essential for managing chronic conditions effectively. By identifying subtle changes in health parameters, AI can alert healthcare providers to potential problems before they escalate, leading to quicker interventions and better outcomes. This proactive approach is key to improving the quality of life for individuals living with chronic diseases.
Enhanced Accessibility and Affordability
AI-driven tools and platforms can potentially increase access to healthcare services, particularly in underserved communities. Telemedicine platforms powered by AI can provide remote consultations, diagnostics, and monitoring, making specialized care more readily available to those in geographically remote areas or those with limited mobility. Furthermore, the potential for automated tasks and streamlined workflows can significantly reduce the cost of healthcare, making chronic disease management more affordable for a wider range of patients.
Ethical Considerations and Data Security
The integration of AI in chronic disease management raises important ethical considerations regarding data privacy and security. Robust data governance frameworks and security protocols are essential to protect patient confidentiality and ensure responsible use of sensitive medical information. Transparency and accountability in AI algorithms are crucial to build trust and ensure that these systems are fair and equitable for all. Addressing these ethical challenges is paramount to realizing the full potential of AI in healthcare.